Technorati Tags: Nanofibers or Nanotubes and Nano or Nanotechnology and nanoparticles or Nanotech and Nanopore or nanochemistry and nanoscale or nanowires and nanogenerators or Neoproteoglycans and Biotechnology or heparin and nanostructures or Nanoscience
Blood-Compatible Nanoscale Materials Possible Using Heparin
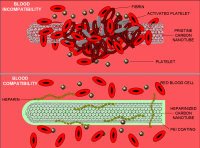 | Caption: Image displays blood compatibility of carbon nanotube when coated with heparin. Credit: Rensselaer/Robert Linhardt, Usage Restrictions: Credit: Rensselaer/Robert Linhardt. |
TROY, N.Y. — Researchers from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have engineered nanoscale materials that are blood compatible using heparin, an anticoagulant. The heparin biomaterials have potential for use as medical devices and in medical treatments such as kidney dialysis.
The researchers prepared several materials with heparin composites or coatings, including carbon nanotubes, nanofibers, and membranes with nanosized pores, and then demonstrated the materials’ high compatibility with blood. Heparin is a common therapeutic used to maintain blood flow or prevent clotting during medical procedures and treatments.
The researchers demonstrated the composite heparin membrane with nanopores could work as an artificial kidney, or dialyzer, by filtering the blood and maintaining its flow. The presence of this blood-compatible dialyzer could potentially eliminate the need for systemic administration of heparin to the patient during kidney dialysis, the researchers say.
The heparin-coated membranes are described in a paper titled “Ionic Liquid-Derived Blood Compatible Membranes for Kidney Dialysis,” published online Apr. 24 in advance of print in the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research.
“These heparin composite membranes and fibers and coated carbon nanotubes are an enabling technology,” says Saravanababu Murugesan, a recent doctoral graduate in chemical and biological engineering at Rensselaer and lead author of the paper. “Our results show these novel materials have great promise in the development of improved medical devices that are blood compatible.”
The research team is led by Robert Linhardt, the Ann and John H. Broadbent Jr. ’59 Senior Constellation Professor of Biocatalysis and Metabolic Engineering at Rensselaer, and includes collaboration with Pulickel Ajayan, the Henry Burlage Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, and Omkaram “Om” Nalamasu, professor of materials science and engineering, at Rensselaer. Additional co-authors of the paper are Shaker Mousa, director of the Pharmaceutical Research Institute at Albany College of Pharmacy, and Aravind Vijayaraghavan, a recent doctoral graduate in materials science and engineering at Rensselaer. Funding for this research was provided by the National Institutes of Health.
Recent results related to this work have been published online in the journals Langmuir (“Blood Compatible Nanotubes – Nano-based Neoproteoglycans,” Mar. 11, 2006) and Biomacromolecules (“Preparation of Biopolymer Fibers by Electrospinning from Room Temperature Ionic Liquids,” Jan. 26, 2006). Provisional patents have been filed by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
Research in Linhardt’s group at the Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies at Rensselaer focuses on complex carbohydrates such as heparin. After determining the structure of these molecules, researchers study their biological activities to establish a structure-activity relationship that may reveal lead compounds for new drug development. Recent discoveries include a synthetic method for preparation of heparin in quantities large enough for use in medical treatment.
Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies at RensselaerAt Rensselaer, faculty and students in diverse academic and research disciplines are collaborating at the intersection of the life sciences, the physical sciences, and engineering to encourage discovery and innovation. Rensselaer’s four biotechnology research constellations - biocatalysis and metabolic engineering, functional tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, biocomputation and bioinformatics, and integrative systems biology - engage a multidisciplinary mix of faculty and students focused on the application of engineering and physical and information sciences to the life sciences. Ranked among the world’s most advanced research facilities, the Center for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Studies at Rensselaer provides a state-of-the-art platform for collaborative research and world-class programs and symposia.
About Rensselaer: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, founded in 1824, is the nation’s oldest technological university. The university offers bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees in engineering, the sciences, information technology, architecture, management, and the humanities and social sciences. Institute programs serve undergraduates, graduate students, and working professionals around the world. Rensselaer faculty are known for pre-eminence in research conducted in a wide range of fields, with particular emphasis in biotechnology, nanotechnology, information technology, and the media arts and technology. The Institute is well known for its success in the transfer of technology from the laboratory to the marketplace so that new discoveries and inventions benefit human life, protect the environment, and strengthen economic development.
Contact: Tiffany Lohwater lohwat@rpi.edu 518-276-6542 Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Related: Keyword Nanotech Sunday, Sunday, April 30, 2006 Micro-pump is cool idea for future computer chips, Sunday, April 16, 2006 Self-Powered Nanoscale Devices, Sunday, April 09, 2006 Nanopore Method Genome Sequencing, Sunday, April 02, 2006 Quantum dot method rapidly identifies bacteria, March 26, 2006 'Custom' nanoparticles, cancer diagnosis and treatment, Sunday, March 26, 2006, Green nanochemistry, American Chemical Society symposium, Sunday, March 19, 2006 nanotechnologists demonstrate artificial muscles powered by highly energetic fuels, Sunday, Sunday, March 12, 2006 magnetic phenomenon may improve RAM memories, February 26, 2006 Nanoscience study shows that quantum dots 'talk', Sunday, February 26, 2006 Nano-bots to undertake major tasks?, Sunday, February 19, 2006 Nanotech to improve health care delivery, Sunday, February 19, 2006 nano-canary in the nanotoxicology coalmine, Sunday, December 04, 2005 Nano-cages 'fill up' with hydrogen, Sunday, November 13, 2005 Testing toxicity of nanomaterials, Sunday, October 23, 2005 single-molecule car, 'Nanocar', Sunday, August 28, 2005 Writing at the nanoscale, Thursday, May 26, 2005 discontinuous palladium, siloxane self-assembled monolayer, Sunday, May 08, 2005 Center for Nanoscale Materials, Monday, April 25, 2005 Nanomagnets, Nanocomposite, Monday, March 21, 2005 porphyrin tubes may lead to new nanodevices, inexpensive hydrogen fuel








No comments:
Post a Comment