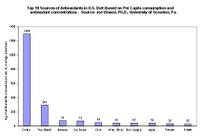
Coffee is number one source of antioxidants
Their study was described today at the 230th national meeting of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society."Americans get more of their antioxidants from coffee than any other dietary source. Nothing else comes close," says study leader Joe Vinson, Ph.D., a chemistry professor at the university. Although fruits and vegetables are generally promoted as good sources of antioxidants, the new finding is surprising because it represents the first time that coffee has been shown to be the primary source from which most Americans get their antioxidants, Vinson says. Both caffeinated and decaf versions appear to provide similar antioxidant levels, he adds.
He cautions that high antioxidant levels in foods and beverages don't necessarily translate into levels found in the body. The potential health benefits of these antioxidants ultimately depends on how they are absorbed and utilized in the body, a process that is still poorly understood, says Vinson, whose study was primarily funded by the American Cocoa Research Institute.
The news follows a growing number of reports touting the potential health benefits of drinking coffee. It also comes at an appropriate time: Coffee consumption is on the rise in the United States and over half of Americans drink it everyday, according to the National Coffee Association.
Antioxidants in general have been linked to a number of potential health benefits, including protection against heart disease and cancer. For the current study, Vinson and his associates analyzed the antioxidant content of more than 100 different food items, including vegetables, fruits, nuts, spices, oils and common beverages. The data was compared to an existing U.S. Department of Agriculture database on the contribution of each type of food item to the average estimated U.S. per capita consumption.
Coffee came out on top, on the combined basis of both antioxidants per serving size and frequency of consumption, Vinson says. Java easily outranked such popular antioxidant sources as tea, milk, chocolate and cranberries, he says. Of all the foods and beverages studied, dates actually have the most antioxidants of all based solely on serving size, according to Vinson. But since dates are not consumed at anywhere near the level of coffee, the blue ribbon goes to our favorite morning pick-me-up as the number one source of antioxidants, he says.
Besides keeping you alert and awake, coffee has been linked to an increasing number of potential health benefits, including protection against liver and colon cancer, type 2 diabetes, and Parkinson's disease, according to some recently published studies. But there's also a downside: Java can make you jittery and cause stomach pains, while some studies have tied it to elevated blood pressure and heart rates. More research is needed, particularly human studies, to firmly establish its health benefits, Vinson says.
While the findings would seem to encourage people to go out and drink more coffee, Vinson emphasizes moderation. "One to two cups a day appear to be beneficial," he says. If you don't like coffee, consider drinking black tea, which is the second most consumed antioxidant source in the U.S. diet, Vinson says. Bananas, dry beans and corn placed third, fourth and fifth, respectively.
But don't forget about fresh fruits and veggies, the researcher cautions. "Unfortunately, consumers are still not eating enough fruits and vegetables, which are better for you from an overall nutritional point of view due to their higher content of vitamins, minerals and fiber," Vinson says. Dates, cranberries and red grapes are among the top fruits for antioxidants on the basis of concentration (antioxidants per serving size), he says.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization, chartered by the U.S. Congress, with a multidisciplinary membership of more than 158,000 chemists and chemical engineers. It publishes numerous scientific journals and databases, convenes major research conferences and provides educational, science policy and career programs in chemistry. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio. ###
The paper on this research, AGFD 10, will be presented at 8:30 a.m., Sunday, Aug. 28, at the Washington Convention Center, Room 203A, during the symposium "The Potential Health Benefits of Antioxidants."
Joe A. Vinson, Ph.D., is a professor of chemistry at the University of Scranton in Scranton, Pa.
Contact: Charmayne Marsh Michael Bernstein 202-872-4400 202-249-4137 (Aug. 27 - Sept. 1) American Chemical Society
more at Coffee or antioxidants and Health or Science and chemistry